Lapisan bubuk adalah proses yang disetel halus yang sangat bergantung pada presisi bahan baku dan teknologi pengolahan. Setiap komponen - resin, agen pengeras, pigmen, pengisi, dan aditif - harus dipilih dan ditangani dengan kontrol yang ketat untuk memastikan tidak hanya daya tarik estetika tetapi juga daya tahan jangka panjang dari finish.
Terutama dalam pengaturan industri di mana lapisan menghadapi cuaca, paparan kimia, atau stres mekanis, lapisan bubuk presisi tergantung pada sinergi formulasi dan peralatan.
Jenis Resin Utama yang Digunakan dalam Lapisan Bubuk
Resin Poliester Thermosetting
Ideal untuk aplikasi luar ruangan, resin poliester thermosetting memberikan ketahanan cuaca yang sangat baik. Kinerja mereka sangat tergantung pada konsistensi ukuran partikel, yang secara langsung mempengaruhi kelancaran film dan keseragaman pengerasan.
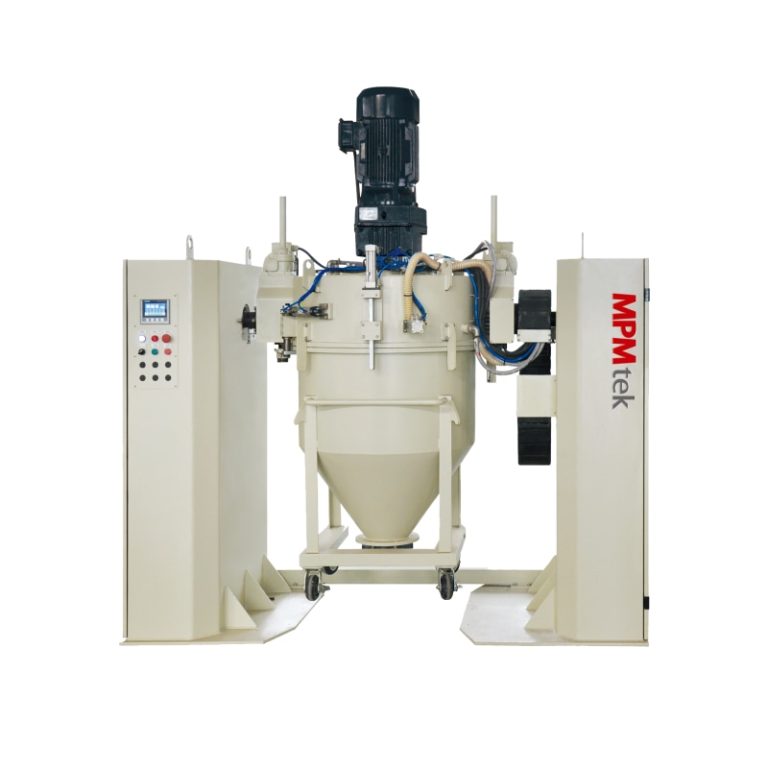
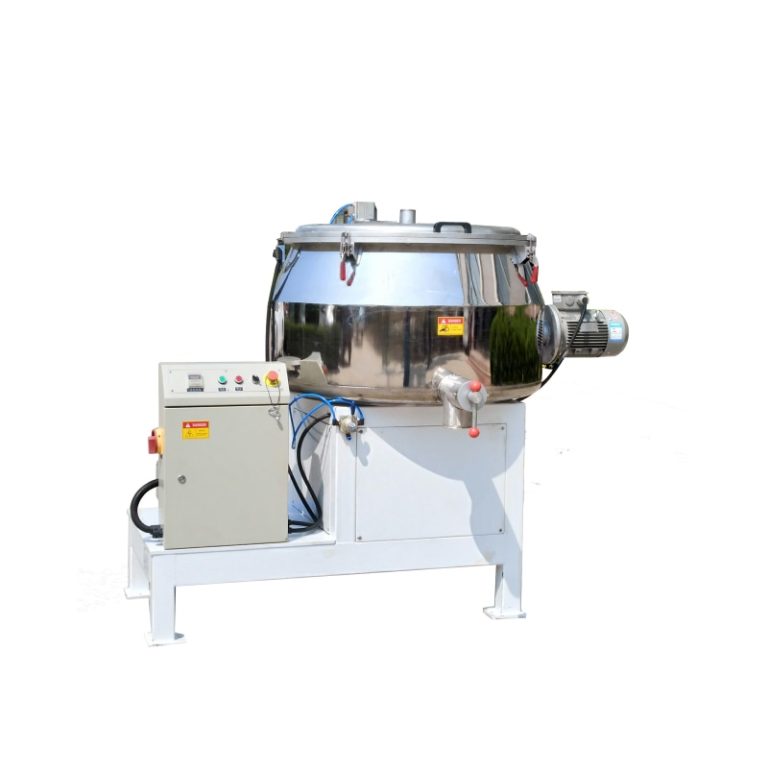
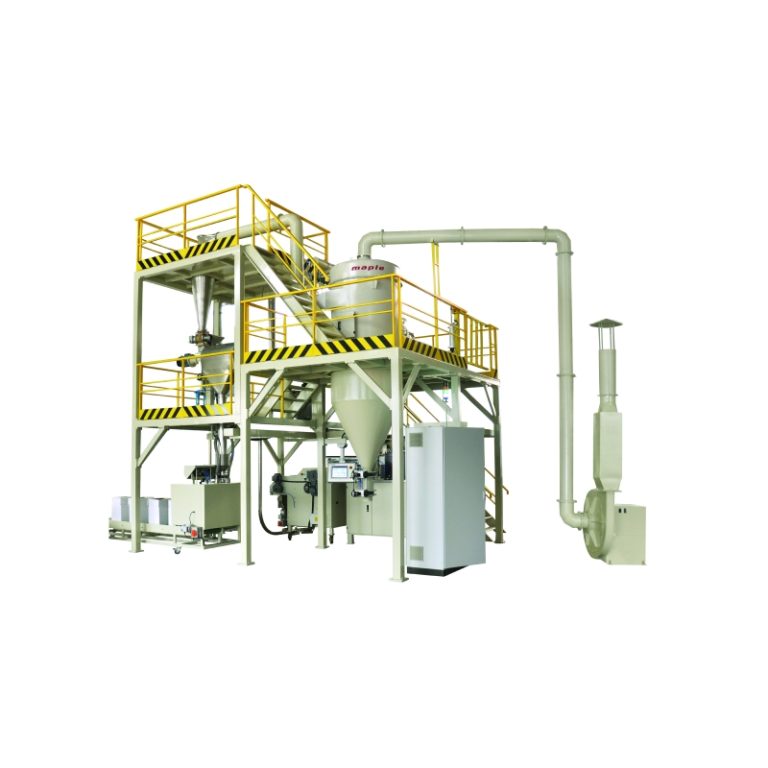
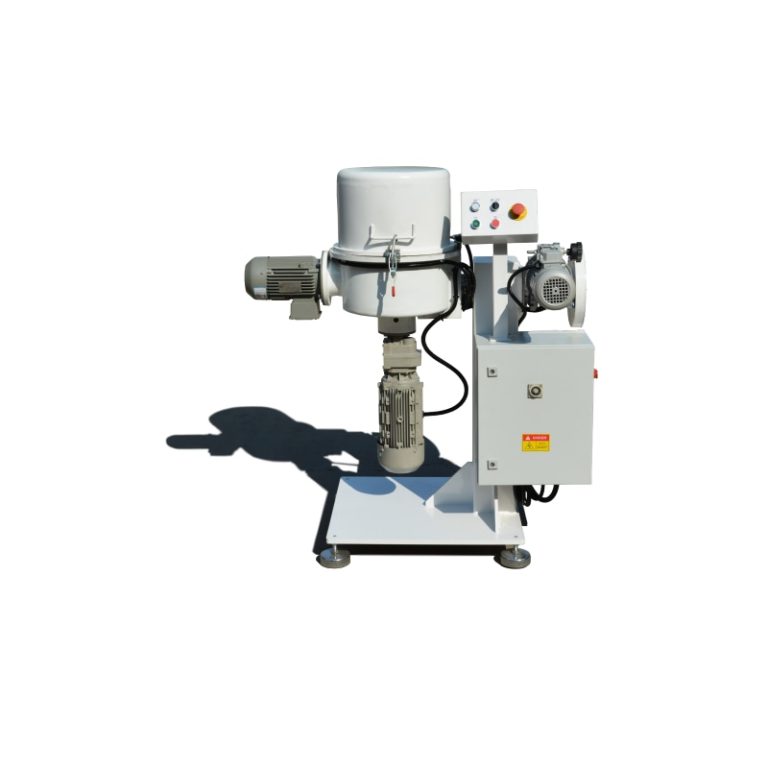
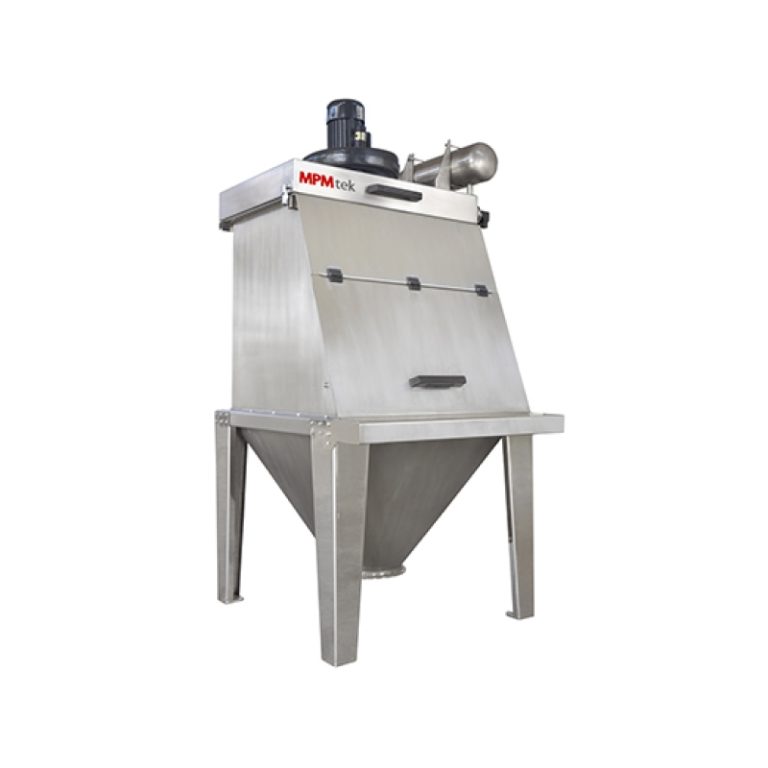
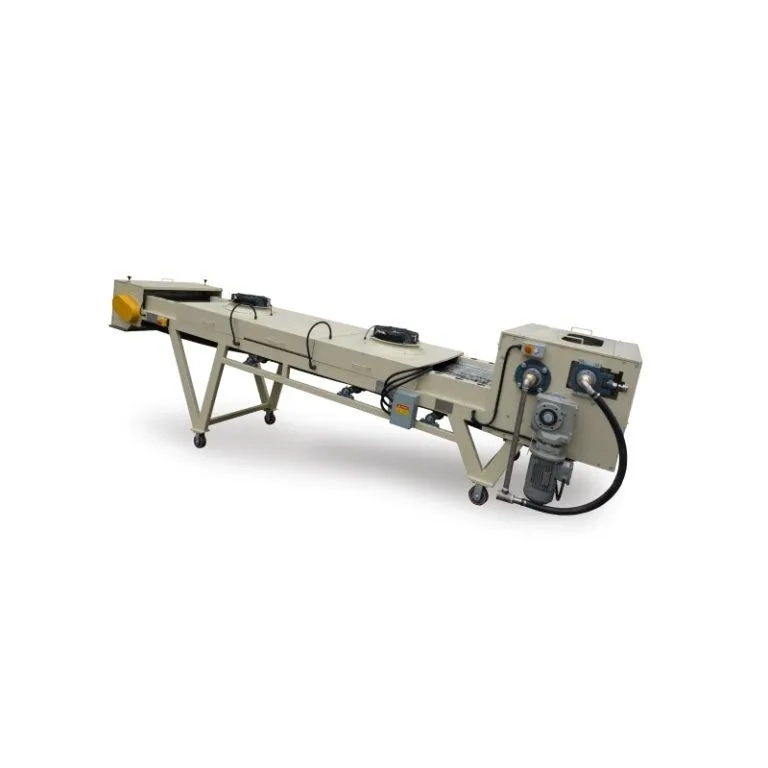
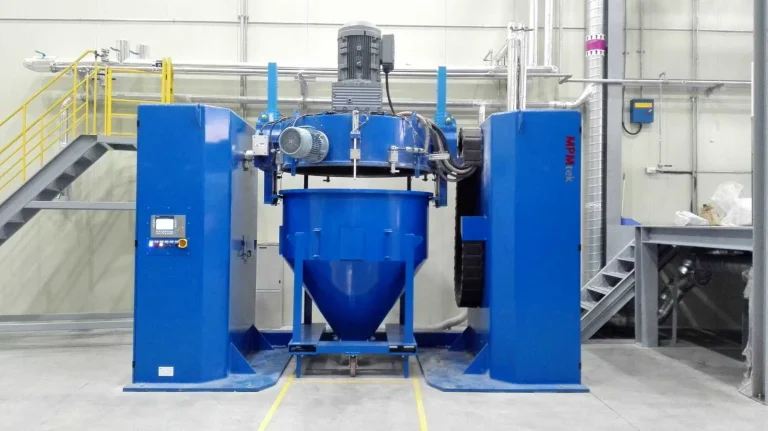
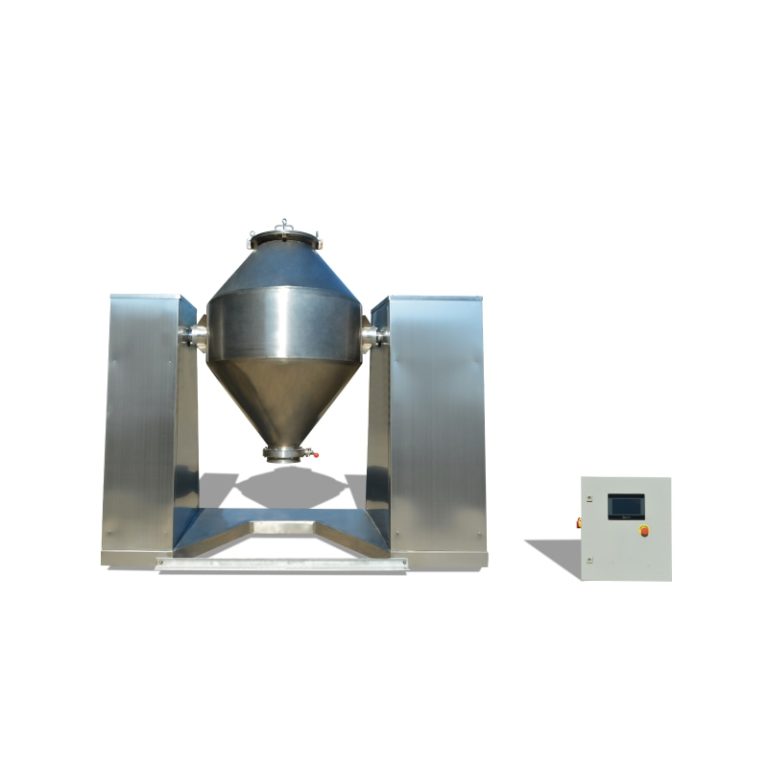
Untuk memastikan dispersi optimal, pencampur wadah seperti Pengcampur Kontainer adalah mesin pencampuran offline dengan wadah bergerak, menggunakan untuk mencampur bahan baku. Pengaturan ini memungkinkan pencampuran resin seragam sebelum ekstrusi. Selain itu, mikronisasi diperlukan untuk menyempurnakan ukuran partikel untuk transfer elektrostatik yang lebih baik.
Resin Berbasis Epoksi
Resin epoksi disukai untuk lingkungan interior karena adhesi dan ketahanan kimia yang unggul. Liputan tepi, terutama dalam geometri kompleks, meningkat dengan ukuran partikel yang dikendalikan.
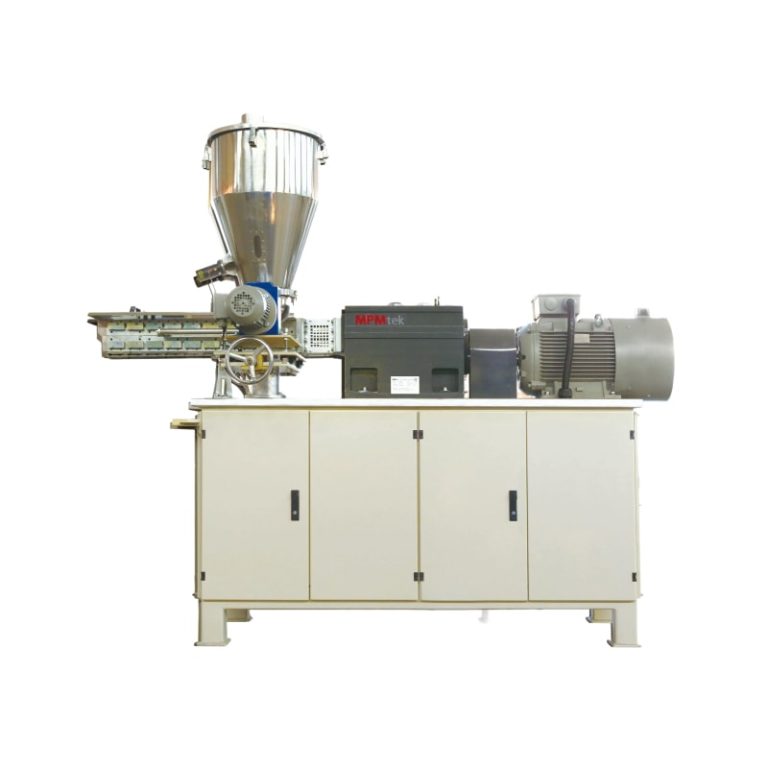
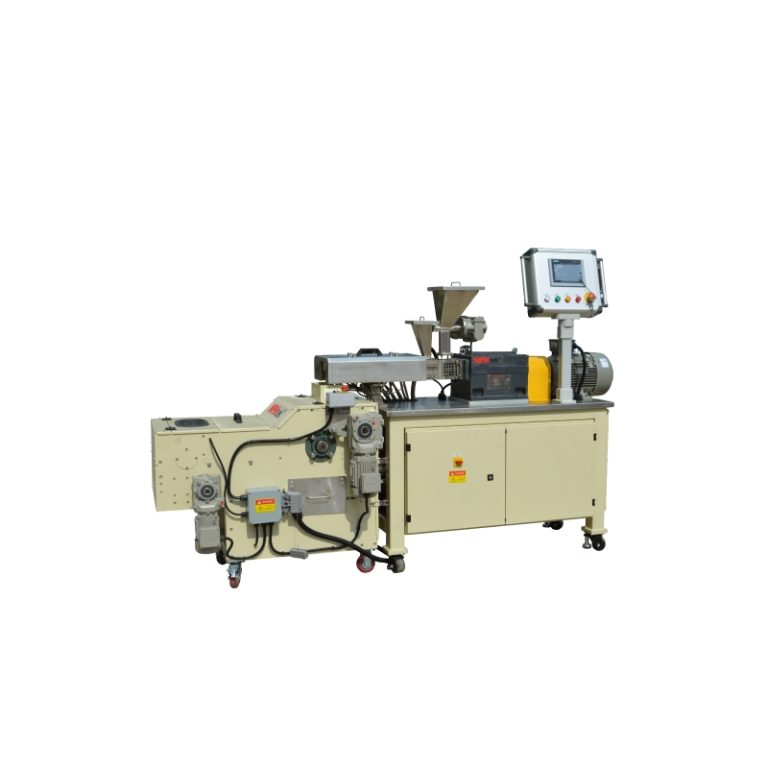
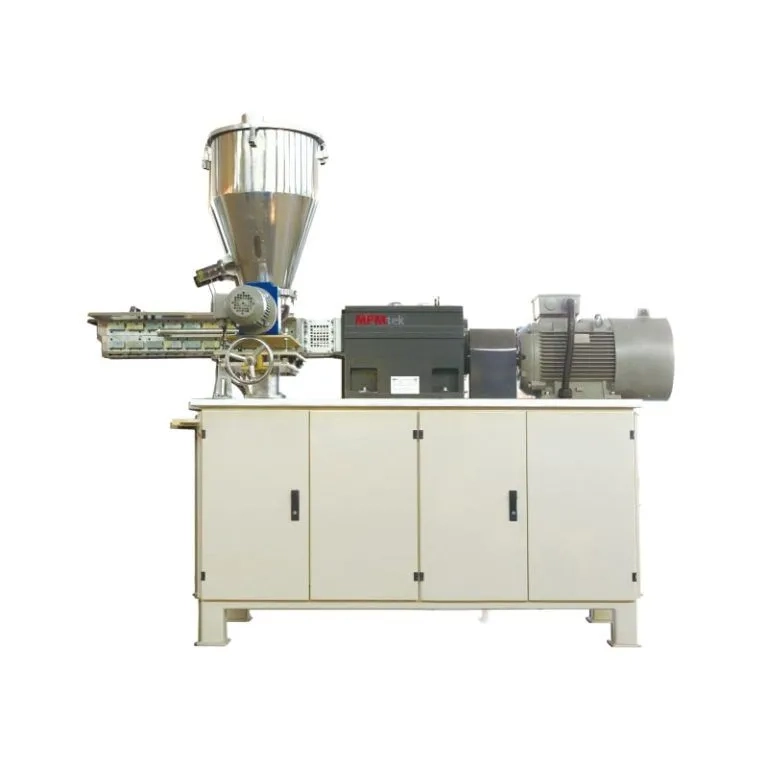
Selama pemrosesan, stabilitas termal adalah masalah. yang Kembar sekrup extruder adalah peralatan yang sangat penting untuk pengolahan lapisan bubuk karena memastikan pencampuran lebur homogen pada suhu yang terkontrol dengan tepat, menghindari degradasi.
Sistem Resin Hibrid
Menggabungkan resin poliester dan epoksi menghasilkan sifat mekanis yang seimbang yang cocok untuk lapisan tujuan umum. Dispersi yang konsisten sangat penting di sini - terutama di berbagai batch produksi.
Mencampur secara efisien dan homogen, seperti yang dicapai melalui mixer wadah, mempertahankan keseragaman. Untuk efisiensi aplikasi, distribusi ukuran partikel harus disetel halus untuk mengurangi kerugian selama penyemprotan elektrostatik.
Agen Pengobatan dalam Formulasi Lapisan Bubuk
Dicyandiamide dan Amine Derivatif
Ini biasanya digunakan dengan sistem epoksi dan memungkinkan pengerasan suhu sedang. Ukuran partikel yang lebih kecil dapat mempercepat reaksi silang, tetapi mereka harus dicampur secara merata untuk mencegah inkonsistensi penyembuhan.
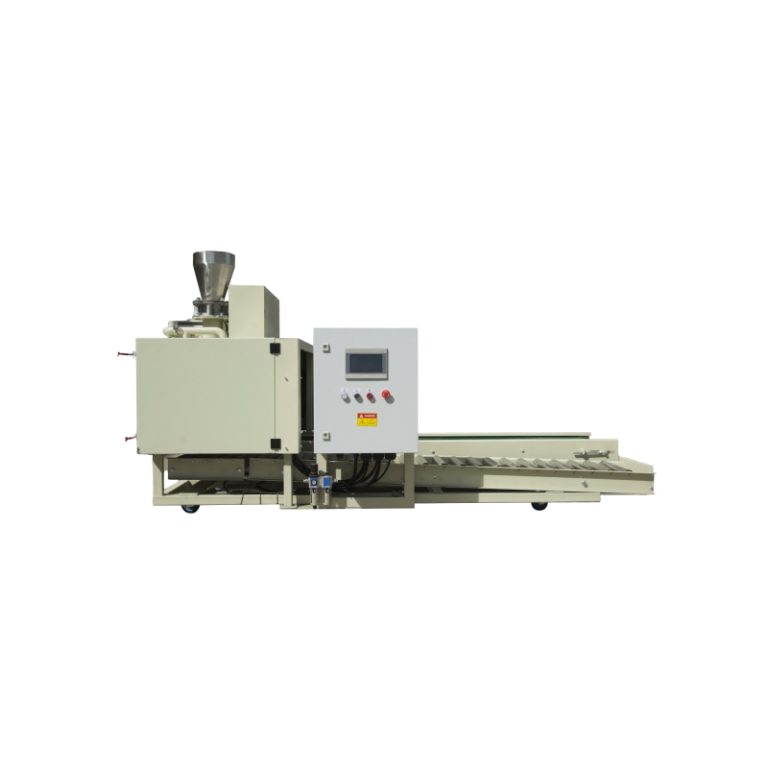
Pengumpan sekrup kembar dipaksa memberi makan bahan dengan fluiditas buruk dan gravitasi spesifik rendah, membuatnya ideal untuk mencapai distribusi agen ini yang konsisten.
Senyawa TGIC dan HAA
Digunakan dengan resin poliester, agen pengeras ini menawarkan ketahanan UV dan fleksibilitas yang tinggi. Mikronisasi yang tepat meningkatkan kontrol gloss. Sistem pakan terintegrasi MPMtek mendukung penggabungan agen yang tepat ke dalam formulasi dasar, meminimalkan variabilitas dan memastikan sifat film yang konsisten di seluruh produksi.
Pengekas Berbasis Uretdione
Pengekas ini memiliki fungsionalitas isosianat yang diblokir dan berguna dalam proses pengerasan suhu rendah. Mereka membutuhkan keseragaman partikel yang stabil untuk menghindari reaksi dini selama penyimpanan.
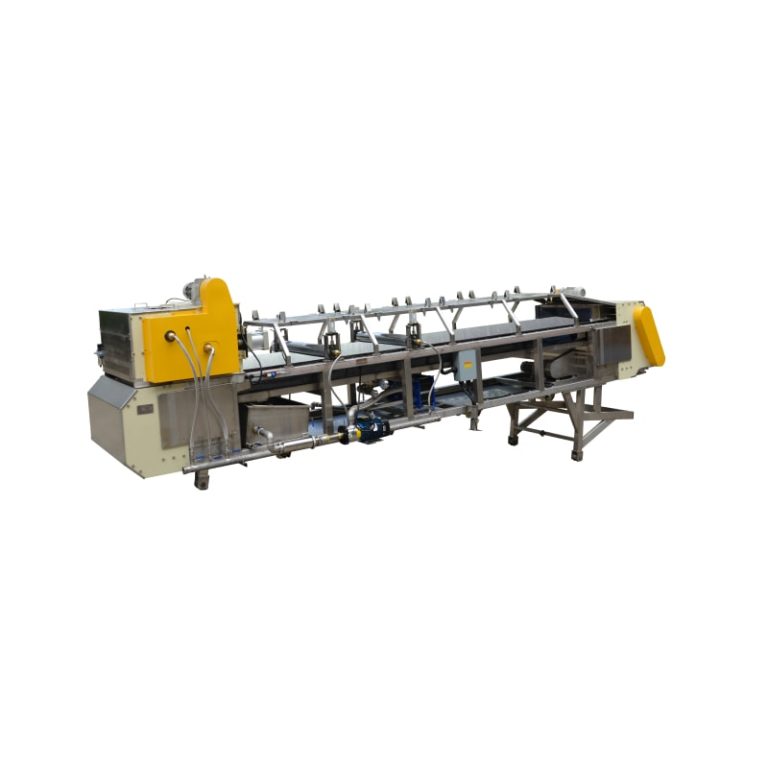
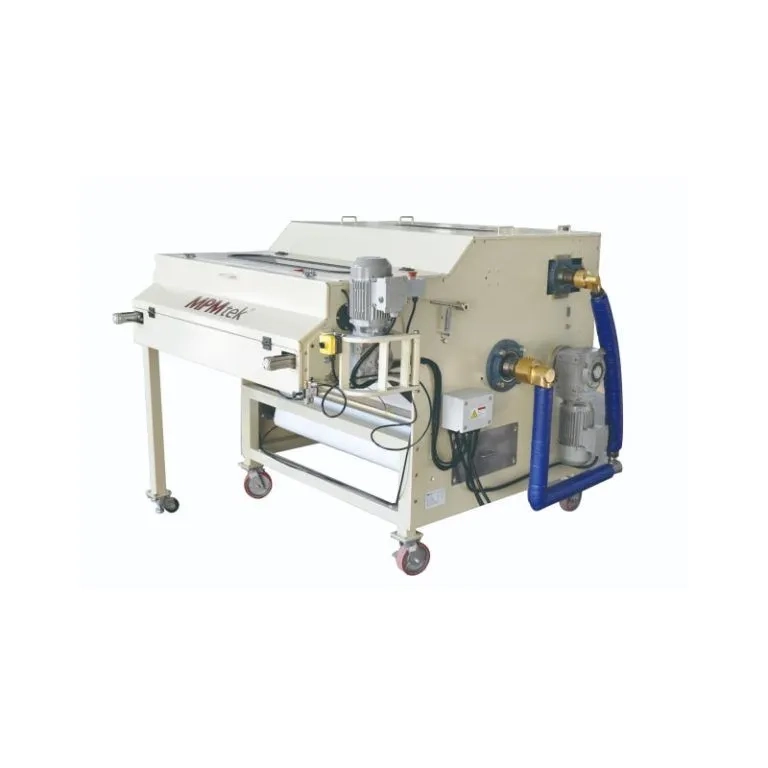
Sistem pendinginan seperti Sabuk Pendinginan Udara terdiri dari rol pendingin, konveyor rantai baja tahan karat, penghancur dan sistem udara pendingin memastikan bahwa bahan diproses di bawah ambang dekomposisi.
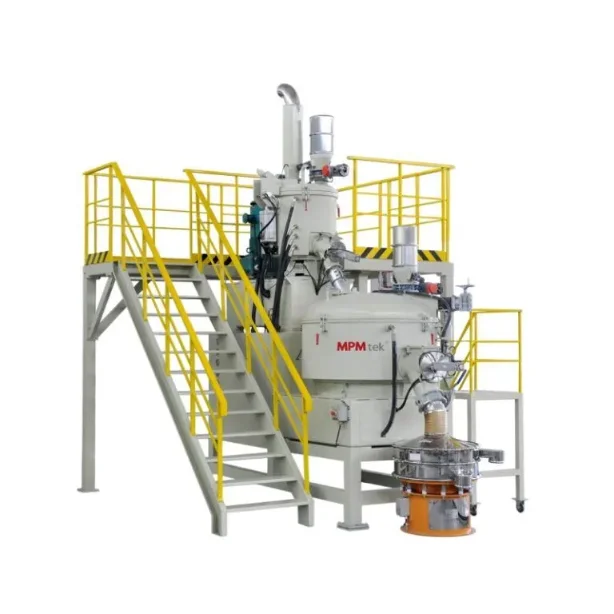

Pigment dalam Kinerja Lapisan Bubuk
Pigment anorganik
Dikenal karena opasitas dan ketahanan panas mereka, pigmen anorganik adalah pusat untuk lapisan kelas industri. Aglomerasi selama ekstrusi dapat merusak tingkat gloss.
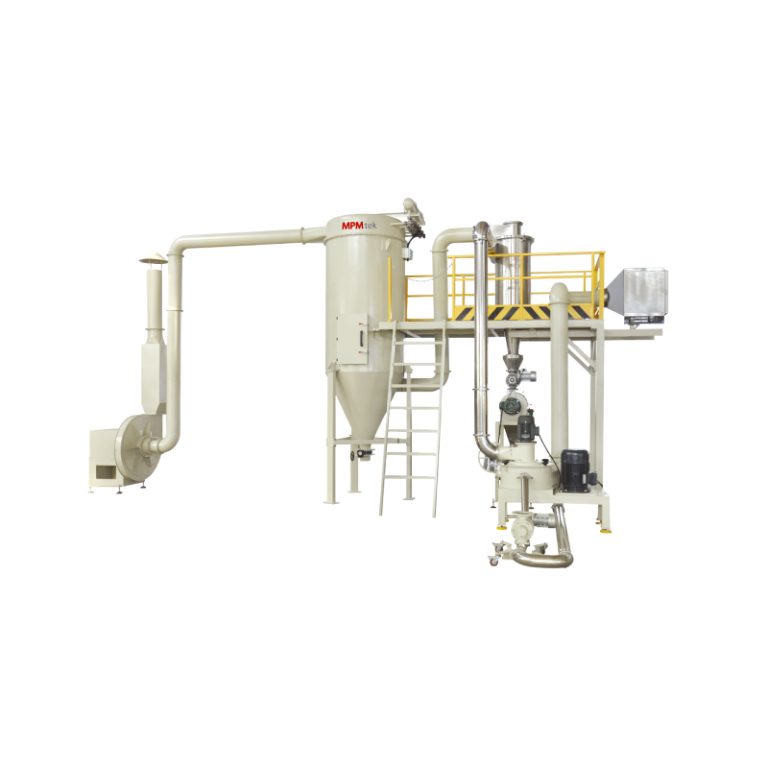
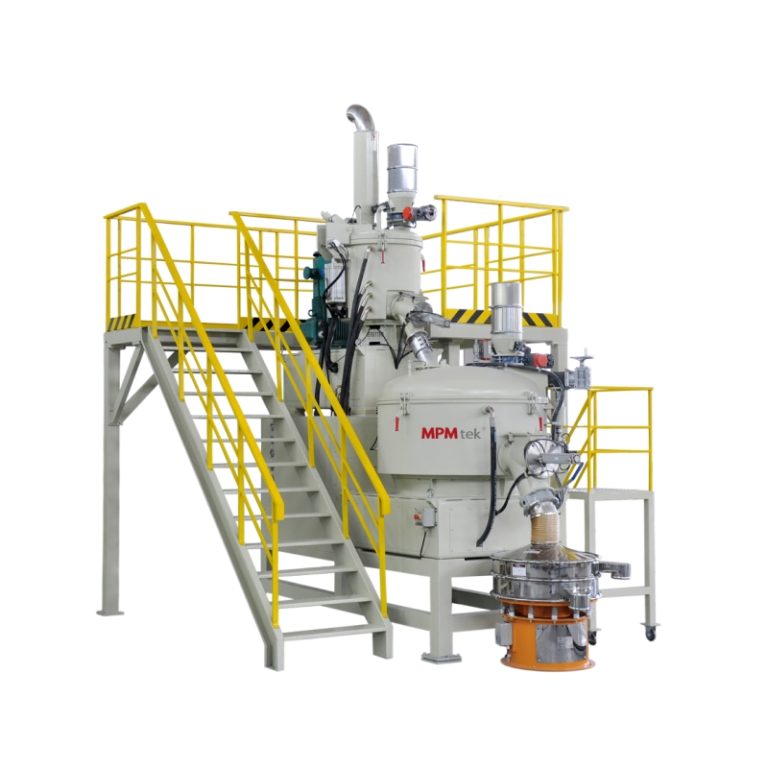
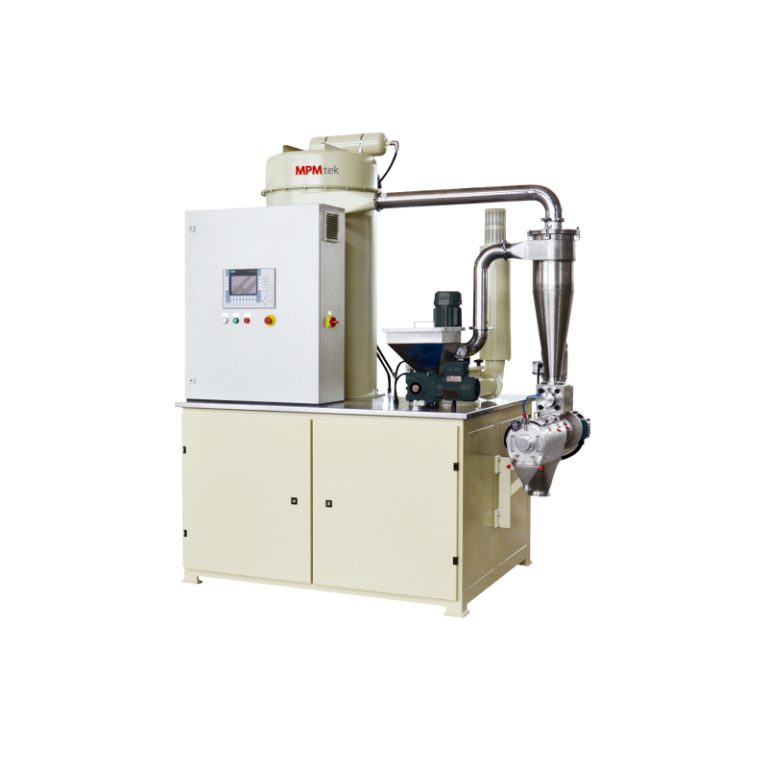
Itulah sebabnya mengapa ACM Micro Grinding System terdiri dari pabrik pengklasifikasi udara kecepatan tinggi, menawarkan kontrol yang ketat atas dispersi pigmen tanpa mengorbankan kualitas selesai.
Pigment Organik
Pigment ini memberikan warna yang cerah tetapi lebih sensitif selama pemrosesan. Kontrol intensitas geser sangat penting untuk mempertahankan kekuatan warna tanpa merusak integritas pigmen.
Peralatan seperti mixer wadah, yang menggunakan pengaduk dan penghancur kecepatan tinggi sementara kepala pencampuran miring 180 derajat ke posisi kerja, memberikan fleksibilitas yang diperlukan dalam menangani bahan halus ini.
Pigment Efek (Metallics & Pearlescents)
Untuk aplikasi yang membutuhkan kedalaman visual atau kilau logam, pigmen efek harus seragam diikat pada partikel bubuk untuk mencegah pemisahan atau berwarna-warni. yang Mixer Ikatan Logam berfungsi untuk mengikat cat logam ke permukaan partikel lapisan bubuk dengan gloss logam.
Teknologi ini memastikan distribusi merata pigmen logam sambil melindungi sifat reflektifnya.
Pengisi Mengubah Sifat Lapisan Bubuk
Pengisi Barium Sulfat dan Kalsium Karbonat
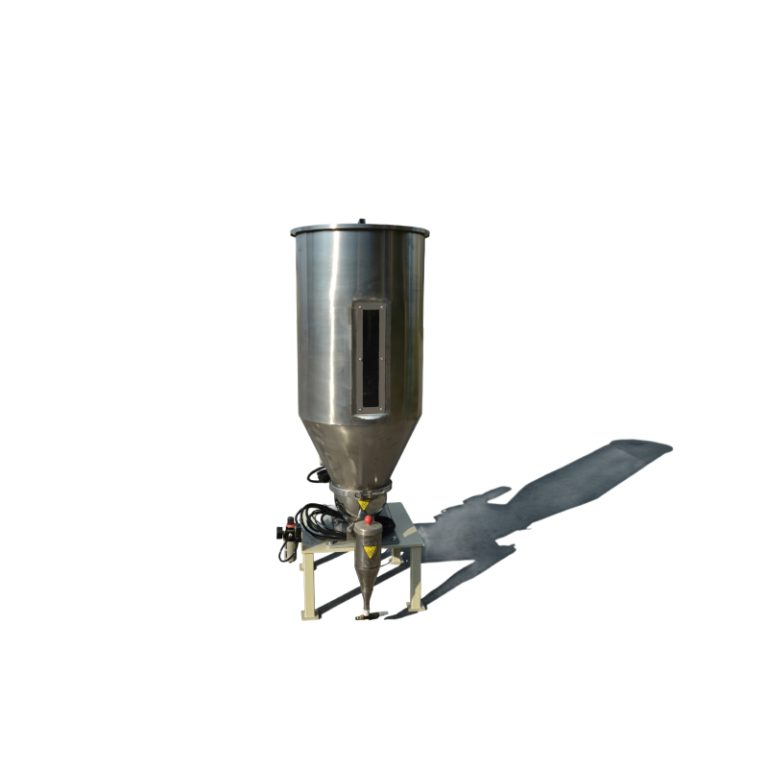
Pengisi ini meningkatkan kekerasan dan mengurangi biaya formulasi. Namun, dampaknya pada viskositas membuat pemberian makan presisi sangat penting. Pengumpan volumetrik dari MPMtek meningkatkan kontrol throughput, memungkinkan dosis yang akurat yang mempertahankan aliran lapisan.
Pengisi berbasis silika (amorf atau berasap)
Digunakan untuk anti caking dan modifikasi permukaan, pengisi silika harus ultra halus dan konsisten tersebar. Sistem loop tertutup yang dilengkapi dengan pemantauan real time membantu mencegah pengekumpulan dan memastikan perilaku seragam di seluruh batch.
Fungsi Aditif dalam Sistem Lapisan Bubuk
Aliran Modifikator dan Degasing Agen
Agen ini mencegah cacat visual dengan mengendalikan dinamika lebur selama pengerasan. Aditif skala nanometer harus dosis dengan hati-hati. Pengumpan sekrup kembar untuk pakan aditif menawarkan akurasi hingga volume kecil sambil menjaga konsistensi aliran melalui pengaduk internal.
Agen Kontrol Biaya
Aditif ini mengatur seberapa baik bubuk menempel pada substrat logam selama aplikasi elektrostatik. Garis pencampuran terintegrasi membantu menjaga distribusi rata agen ini tanpa mengkompromikan bahan baku lainnya.
Stabilizer UV dan Antioksidan
Perlindungan terhadap sinar matahari dan oksidasi sangat penting untuk lapisan umur panjang. Untuk aditif sensitif seperti ini, kondisi pengolahan inert mungkin diperlukan - Seluruh pengolahan dikendalikan oleh sistem perkiraan dan kontrol cerdas dalam MPMteksistem ikatan laboratorium mendukung jenis lingkungan yang dikendalikan ini.
Kontrol Ukuran Partikel dalam Produksi Lapisan Bubuk
Ukuran partikel mempengaruhi hampir setiap tahap proses lapisan bubuk:
| Daerah dampak | Pentingnya Ukuran Partikel |
| Deposisi Elektrostatik | Ukuran seragam meningkatkan efisiensi transfer; partikel besar mengurangi tingkat deposisi |
| Permukaan Selesai | Bahkan aliran lebur partikel mengarah ke selesai yang lebih halus; inkonsistensi menyebabkan kulit jeruk |
| Penyimpanan & Aliran | Ukuran yang tepat menghindari pengelompokan; Membantu menjaga mobilitas selama penyimpanan |
Sistem penggilingan mikro ACM juga dapat digunakan untuk menggiling pigmen Distribusi ukuran partikel yang sempurna dari lapisan bubuk dapat diperoleh dengan mengatur parameter berjalan.
Pemilihan Peralatan yang Mempengaruhi Pengolahan Bahan Baku
- Homogenitas pencampuran pra sangat penting; memastikan semua proses berikutnya beroperasi pada formulasi dasar yang stabil.
- Bahan-bahan sensitif seperti agen muatan atau antioksidan membutuhkan lingkungan pencampuran yang dikendalikan untuk mempertahankan fungsionalitas.
- Mikronisasi melalui sistem ACM mendefinisikan kualitas bubuk akhir dan memastikan konsistensi transfer selama aplikasi. Lapisan bubuk presisi membutuhkan lebih dari sekedar bahan yang tepat - itu adalah tarian yang kompleks antara ilmu bahan dan teknologi manufaktur. Dengan pengaturan yang tepat, kinerja menjadi dapat diprediksi, dapat diskalakan, dan dapat diandalkan.
FAQ (Pertanyaan umum)
T: Faktor apa yang mempengaruhi pilihan resin dalam lapisan bubuk?
Seleksi resin tergantung pada sifat mekanis yang diinginkan, ketahanan cuaca, ketahanan kimia, dan kompatibilitas substrat.
T: Bagaimana peralatan mempengaruhi kualitas lapisan bubuk?
Peralatan yang tepat memastikan dispersi bahan yang konsisten, dosis yang akurat, profil suhu yang dikendalikan, dan ukuran partikel yang dioptimalkan - semuanya penting untuk mencapai lapisan berkualitas tinggi.
T: Mengapa memilih penyedia mesin khusus seperti MPMtek?
Dengan keahlian di semua tahap produksi lapisan bubuk - dari pra-pencampuran hingga mikronisasi - MPMtek menawarkan solusi mesin yang disesuaikan yang meningkatkan kualitas produk sambil meningkatkan efisiensi operasional untuk produsen di seluruh dunia.